Kotlin Collection 공식 문서를 정리 한 글입니다. Collection의 List / Set / Map에 대한 기초적인 설명을 정리합니다.
Github repo 에서 아래에 적힌 Kotlin 코드들을 확인 하실 수 있습니다.
Collection Overview
- kotlin.collections package 안에 존재
- list안의 item을 elements라고도 표기 함
- Java의 collection을 그대로 가져와서 사용 → 자바 코드와 상호작용 뛰어남
- 하지만, 자바 collection에는 없는 더 많은 operator들을 사용 가능 한데, 이는 확장 함수로 구현 되어 있기 때문
- 자바 collection → 코틀린의 collection
- 자바의 변수 type은 Nullable이 가정 되어 있음 → Item type 체크 안됨 ( platform type으로 변환 됨 )
- 코틀린 collection → 자바 collection
- mutable / immutable 구분 안됨
- Immutable / mutable collection이 존재
- Immutable → collection의 item에 접근 하는것만 허용, 수정에 대한 작업은 서술되어 있지 않음 ( default )
- element를 추가 / 수정 할 일이 있을 때에만 mutable collection을 사용 하라
- JAVA에는 mutable / immutable 으로 collection을 구분 하지 않음에 유의하라
- Mutable → adding / removing등 collection의 item을 수정 하도록 Immutable을 확장 하여 사용
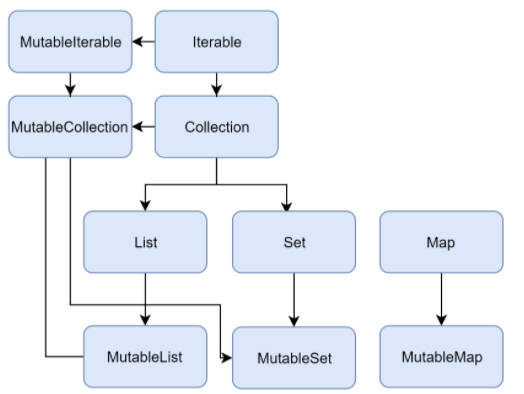
- List
- Index로 값에 접근 하는 순서를 지키는 Collection.
- 중복된 값이 리스트 안에 존재 할 수 있음.
-
두 리스트가 같은 조건 ( == ) → size가 같고, position 마다 동일한 item을 가지고 있으면 두 리스트는 같다고 인지
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10fun checkEqualityOfList() { val bob = Person("Bob", 31) val people = listOf(Person("Adam", 20), bob, bob) val people2 = listOf(Person("Adam", 20), Person("Bob", 31), bob) println(people == people2) bob.age = 32 println(people == people2) } data class Person(val name: String, var age: Int) - array는 초기화 시 배열의 size를 정해 놓지만, list는 사전 정의된 크기는 존재하지 않는다.
- Set
- 고유 값들을 모아놓은 Collection
-
중복된 값이 Set안에 존재 할 수 없음
1
2
3
4
5
6
7fun checkDifferenceWithListAndSet() { val stringList = listOf("one", "two", "one") println("stringList $stringList") val stringSet = setOf("one", "two", "one") println("stringSet = $stringSet") } - null도 담을 수 있다.
-
두 set이 같을 조건 ( == ) → size가 같고, set에 있는 item이 다른 item에도 항상 있는 경우에 두 set이 같다고 인지
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8fun checkEqualityOfSet() { val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4) println("Number of elements: ${numbers.size}") if (numbers.contains(1)) println("1 is in the set") val numbersBackwards = setOf(4, 3, 2, 1) println("The sets are equal: ${numbers == numbersBackwards}") } -
setOf로 set 객체를 생성하는 경우, 기본 구현체로써 LinkedHashSet을 사용 ( insert시 순서 보장 )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7fun checkLinkedHashSet() { val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3, 4) // LinkedHashSet is the default implementation val numbersBackwards = setOf(4, 3, 2, 1) println(numbers.first() == numbersBackwards.first()) println(numbers.first() == numbersBackwards.last()) }
- Map
- Collection interface를 확장 한 collection은 아니지만, collection type으로 간주
- Key-Value pair로 이루어진 dictionary 형태
- Key값은 고유하며, 각 key당 하나의 value만 대응 됨
-
Pair를 item의 형태로 받음
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17fun checkDefaultMap() { val numbersMap = mapOf("key1" to 1, "key2" to 2, "key3" to 3, "key4" to 1) println("All keys: ${numbersMap.keys}") println("All values: ${numbersMap.values}") if ("key2" in numbersMap) println("Value by key \"key2\": ${numbersMap["key2"]}") if (1 in numbersMap.values) println("The value 1 is in the map") if (numbersMap.containsValue(1)) println("The value 1 is in the map") // same as previous } fun mutableMap() { val numbersMap = mutableMapOf("one" to 1, "two" to 2) numbersMap.put("three", 3) numbersMap["one"] = 11 println(numbersMap) } -
mapOf로 map객체를 생성 하는 경우, 기본 구현체로써 LinkedHashMap을 사용 ( insert시 순서 보장 )
1
2
3
4
5
6fun checkEqualityOfMap() { val numbersMap = mapOf("key1" to 1, "key2" to 2, "key3" to 3, "key4" to 1) val anotherMap = mapOf("key2" to 2, "key1" to 1, "key4" to 1, "key3" to 3) println("The maps are equal: ${numbersMap == anotherMap}") }
출처 : https://kotlinlang.org/docs/collections-overview.html
"Android" 카테고리의 최근 포스팅
카테고리 모든 글 보기| Kotlin - 코루틴 동작 원리 ( Continuation / CPS / State Machine ) | 2025. 04. 23 |
|---|---|
| JVM - Runtime Data Area - Thread | 2025. 04. 21 |
| JVM - Runtime Data Area - Heap | 2025. 04. 21 |
| JVM - Runtime Data Area - Method | 2025. 04. 19 |
| JVM - Interned string | 2025. 04. 18 |
| Android - 직렬화 | 2025. 04. 17 |
| Hilt - ComponentScope | 2025. 04. 16 |
| Kotlin - Channel | 2025. 04. 15 |
| Android - ViewModel 에 대해서 | 2025. 04. 14 |
| Android - Bundle 이란 | 2025. 04. 13 |